Example configuration for Fleet SMP
Checklists
Administration: These Work Tickets allow Fleet Administration staff to record and track temporary fuel cards, infringement notices etc
Fleet Procurement: These Work Tickets allow fleet procurement staff to record and track the details of plant, vehicles, and equipment in the commissioning / de-commissioning stages of their life cycle
Housekeeping: These Work Tickets allow Fleet staff to allocate labor hours that are not directly attributable to individual plant items e.g. Workshop maintenance, cleaning tools etc. Housekeeping labor hours are charged against Fleet's overhead budget number
Monthly W/shop Inspection: These Work Tickets are set up specifically for the monthly inspection of a particular workshop. Supervisors are to set up a work ticket against this checklists each time the monthly inspection is carried out
Preventative Maintenance: Services which are scheduled for the Preventative Maintenance Due Report
Scheduled Maintenance: Repairs that are found at the time of a PM Service, Inspection, commissioning, de-commissioning or the fitting of accessories and are scheduled for a later date
Unscheduled Maintenance: This type of repair is not scheduled and is generally considered to be a breakdown or reactive type work that is accompanied by a 'Defect' sheet.
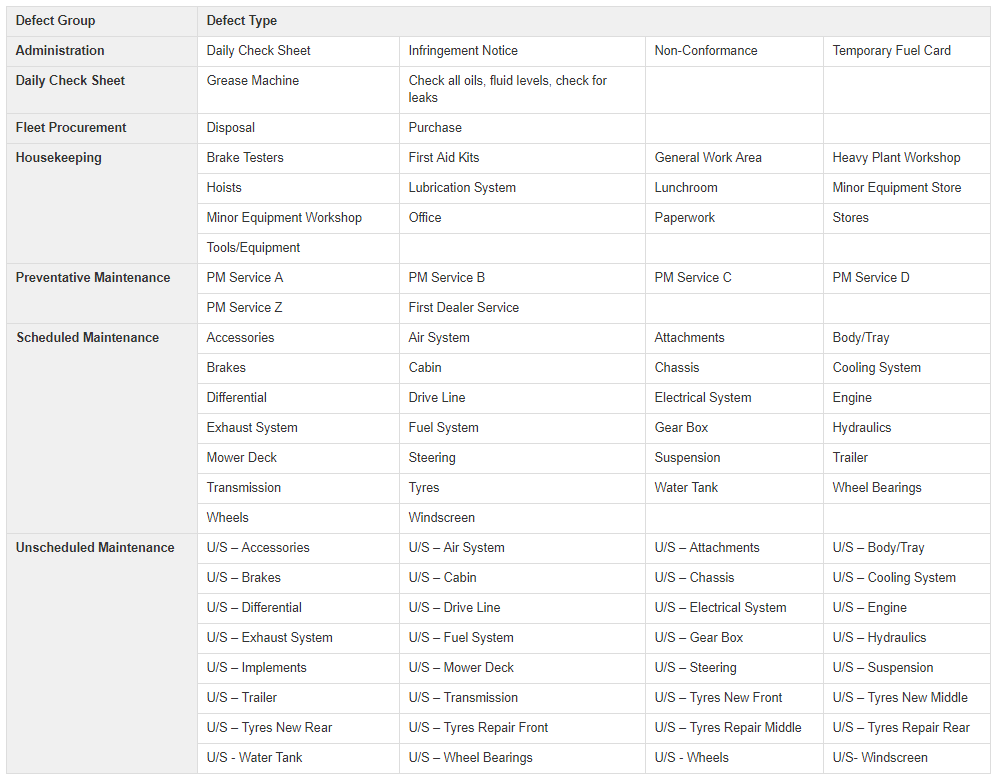
Under each Defect Group, a set of Defect Types have been created.
These have been designed to clearly indicate the type of work that is being carried out on a particular item of plant, vehicle or equipment.
Staff needs to allocate a Defect Type for each and every work ticket that is created.
In designing the work ticket system this way, reports can be generated on an item when assessing it for the Plant Replacement Program and will show up any ongoing issues that item has had.
Below is a table showing all Defect Types under each group:
Cause
The Cause section needs to be completed for each work ticket and Indicates what the Mechanic believes caused the problem to an item of plant, vehicle or equipment. Below is a list of causes that can be adopted by users:
Accident: Indicates when damage has been caused to an item of plant, vehicle or equipment
Design/Manufacturer fault: A defect that is the result of a manufacturing or design fault from the original equipment manufacturer
Incorrect use of plant: Indicates when the driver/operator of the vehicle has used the plant, vehicle or equipment in a way that has caused a defect
Lack of daily maintenance: A defect that is a result of the driver/operator not carrying out their daily inspection checklist resulting in an improperly maintained item of plant, vehicle or equipment
Lack of scheduled maintenance: A defect that has resulted from workshops not carrying out regular maintenance on the vehicle according to the PM Schedule
Mechanical workshop error: A defect that occurs as a result of an error caused by a Workshop
Normal wear & tear: A defect that is the result of normal wear & tear in the plant, vehicle or equipment expected duties
Operator training: A defect that arises during operator training clearly indicating further training
Repairs under warranty: A defect that is identified and rectified within the manufacturer's warranty period
Unfair wear & tear: A defect that is caused by operating the plant, vehicle or equipment in a manner which it was not designed or expected to perform
Vandalism: A defect that is a direct result of Vandalism e.g. Smashed windows, general damage, graffiti, etc
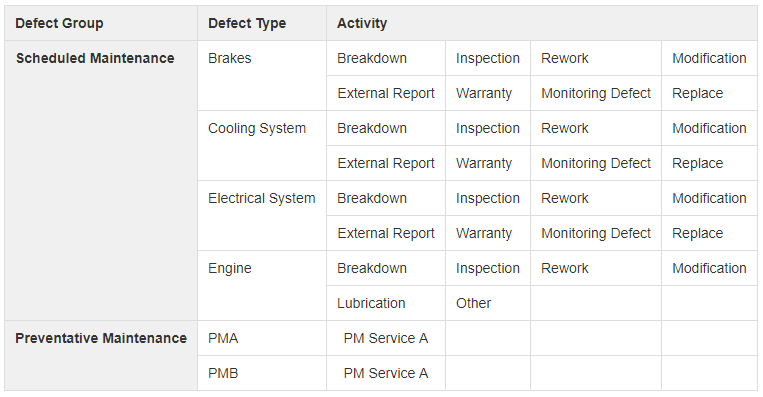
Work activities
When defining activities the list of activities may be common to all Defect Types within a Defect Group, or they may be specific to a subset of Defect Types.
Using a common set of activities simplifies configuration, but using more specific activities may make it easier to create work tickets for the activities to choose from are more specific rather than generic.
Example 1
Repair: To be selected when an operator presents at a Fleet Workshop for unscheduled repairs
External Repair: To be selected when plant, vehicles or equipment are sent to an external service provider for repair
Warranty: To be selected when plant, vehicles, and equipment are repaired under warranty
Inspection: To be selected when performing an inspection of plant, vehicles, equipment, workshop tooling or facilities
Other: To be selected when the work or action required does not fit into other Work Activity categories. A full description of the work undertaken must be provided on the Work Ticket
Paperwork: To be selected when performing paperwork relating to plant, vehicles, equipment, workshop facilities, and operations
Modification: To be selected when modifications are performed on plant, vehicles or equipment
Emergency: To be used when repairs or service is performed during an emergency
Commission: To be selected when new plant, vehicles or equipment are fitted with two ways, lights etc. before going into service
De-Commission: To be selected when two ways, lights, toolboxes etc. are removed from plant, vehicles or equipment prior to disposal
Lubrication: To be selected when plant, vehicles or equipment are lubricated or greased
Rework: To be selected when plant, vehicles or equipment are returned to a workshop for rectification of a previous problem.
Example 2: Specific activities per defect group
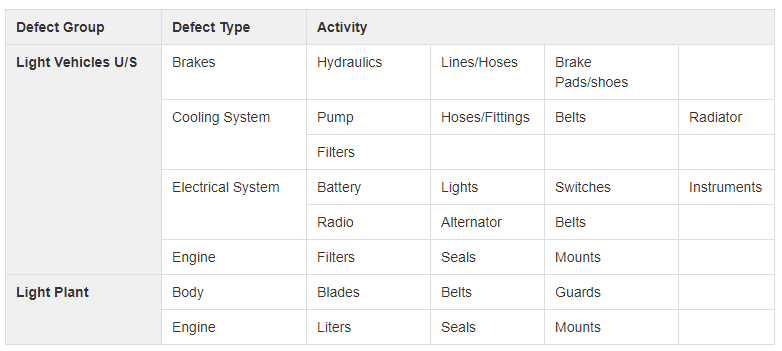
Actions
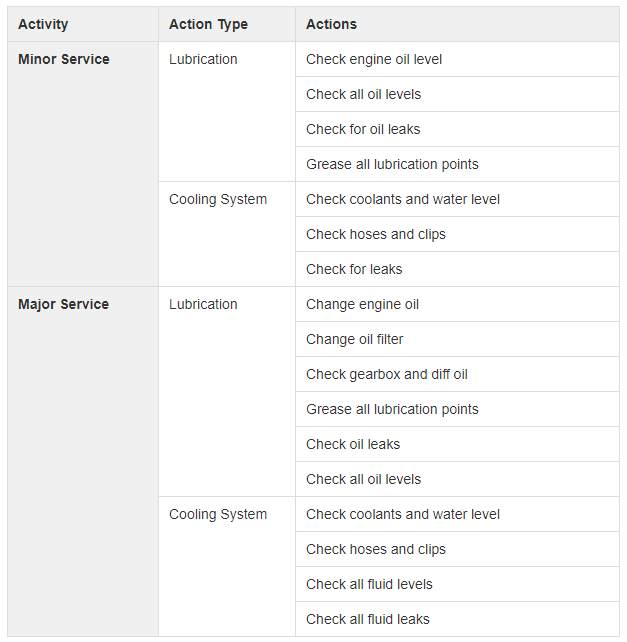
Actions can be configured as the actual work to be performed for a given activity.
In the example below the actions are for a Preventative Maintenance Activity.
Actions are grouped by Action Type.
Table: Sample Actions
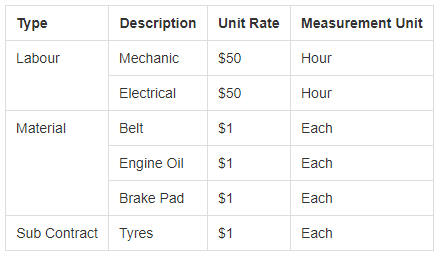
Bill of Quantities
The Bill of Quantities can be used to track costs against a work item.
The costs can be grouped by Labour, Plant, Material, Sub Contract and Other.
In the case of Fleet, it can be used to record the materials (parts) and cost of a maintenance activity.
In Bill of Quantity, the unit rate is fixed for the item which is typical for works with standardized rates.
For Fleet materials, it can be useful to set the unit rate to $1 and then use quantity as the cost since the part cost will differ from plant item to plant item.
Table: Example Bill of Quantities